There are differences exist in how ‘Talent’ is defined across differing sectors and organizations. Some companies prefer to adopt their own definition rather than accepting general definitions. Let’s focus on an active definition for both ‘Talent’ and ‘Talent Management’:
”Talent consists of those individuals who can make a difference to organizational performance either through their immediate contribution or, in the longer-term, by demonstrating the highest levels of potential.“
Basic and simple meaning of Talent could be:
- Ability, aptitude, bent, capacity, endowment, faculty, flair, forte, genius etc.
- Unusual ability to do something well that can be developed by training.
- Person or people with an exceptional ability.
Whereas ”Talent management is a set of business practices or refers to the skills of attracting highly skilled talents, integrating new talents, and developing and retaining current talents to meet current and future business objectives.“
Actually it manage the planning, possession, development, retention and growth of talent who are of particular value to an organization, could be because of their leadership capabilities, prospective for the future, or even because they are satisfying business critical roles and which could actually lead to organizational sustainability, efficiency and excellence in order to achieve business goals.
The term talent management was first cast by McKinsey & Company following a study and gradually its becomes a very useful term when it describes an organization’s commitment to hire, manage and retain talented employees. It embraces all of the work processes and practices that are related to retaining and developing a exclusive workforce.
The process of attracting and retaining effective employees results in increasing competition among the companies because of strategic importance and also known as “The War for Talent.” Talent management which is sometimes also called Human Capital Management is now an essential management practice; before it was exclusively attached to recruitment process while now covers a group of areas. Talent management implies that companies are strategic and conscious in how they source, attract, select, train, develop, retain, promote, and move employees through the organization.
Earlier talent management was often considered with organizing and managing the different talents to have an offer within the organization and this is usually done by studying and evaluating each individual on their skills, talent, personality and character, in order to fill up a particular vacancy within the company. Talents has different skills to offer and the challenge for the companies is to identifying those that fit in with the existing company culture and a effective HR procedures would be able to identify these individuals. Off course it is much beyond that.
Companies are now captivating in a talent management strategy and gradually shifting the responsibility of employees from the human resources sections to all the line managers in the organization. Talent management does give managers a significant role and responsibility in the different processes and in the ongoing development of and retention of exceptional employees. In some organizations, only top probable employees are included in the talent management system while in other companies, every employee is included in the process as equal opportunities.
On the other side talent in an employee can involve all kinds of components, from their educational qualifications and skills, previous experience, strengths and additional training they have undertaken, to their abilities, potential and motive, qualities and personality. Most companies practice talent management in some way, this could be anything from the recruitment of individuals, career planning and opportunities, training and development, performance management and various compensation options and reward for the performers. But how company should involve or practice talent management generally depends on the business strategy, their commitment to employees and other factors. What could be the other components where companies should really focus for the talent management?
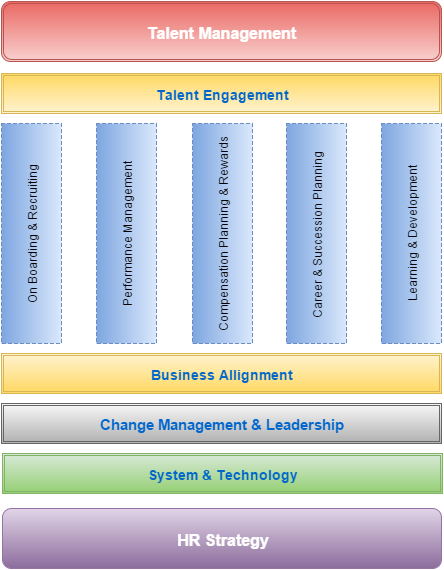
To know this let’s focus on the figure 1 which shows the overview diagram of Talent management? Talent engagement and transformation are top priorities for the leaders now a days and the major challenge is the ability to attract and retain top talent while making sure the existing talents is fully engaged to deliver extraordinary results. For this reason talent engagement is considered to be a crucial factor.
End-to-end talent management encompasses five main pillars: recruitment and onboarding, performance management, compensation planning and rewards, career and Succession Planning and last but not the least learning and development. At some point of time there were four pillars to be considered under talent management but gradually career and succession planning has been updated to make it five.
For a company it is very necessary to have a right business alignment with a mature process for talent strategy and planning. Companies have been extremely successful when they ensure that talent initiatives are aligned with business objectives and business alignment plays a vital role here.
When there is a significant change in the organization, it is necessary to align everyone to support the change drive for the progress. Otherwise, the change would never happen properly. An effective tool for realigning the talents is to have proper change management. It started by capturing the change management goals at the highest level that they apply and communicating them to all those affected. With the right communication and processes, employees can confront extreme organizational changes without a negative impact on business results.
Leaders must have absolute clarity in purpose and focus to avoid business disruption as the reality is that without proper strategy, change is rather a substitution but not evolution. Leadership is therefore considering to be one of the most important component of talent management.
Most companies already use a human resource information system (HRIS) as a repository for employee records and basic information, while many organizations are going a level further by adding talent management systems to their HR technology portfolios. Many experts say talent management systems can help companies attract, retain and develop talents to the mutual benefit of both parties. And in this way the systems and technologies play a vital role in talent management strategy.
Many human resource team finds difficult to develop a talent management strategy that plan out their goals and priorities for the coming future and bind these to their organization’s strategic plan and goals. Often the difficult part is getting started with the right framework for the strategy and plan. The bigger or more challenging the change is to implement, the more we need to align our HR strategy to support it in practical ways. HR strategy actually helps to align all the components together acting as a base for the talent management and hence drive value for the organizations.
And the talent management solutions are the key to build the kind of high-performing talents to establish the success.
Now let us see the overview of five pillars of talent managements.
On Boarding and Recruiting
A exclusive definition of Onboarding from Bersin & Associates states:
“The process of hiring, orienting and immersing employees into their new role and into the organization’s culture.”
The process of adapting new hires and ensuring that they feel welcomed and valued by the organization. This process enables new employees to become productive members of the organization, who understand expectations for their job roles and start understanding the culture of the organization. Onboarding actually goes beyond conventional “orientation” programs which focus mainly on managing policies, forms, and procedures.
So the main purposes of onboarding are typically:
- Help employees to quickly adapt to the company culture and effectual to the business
- Help employees utilize corporate resources and business-specific methodologies and approaches
- Provide a consistent experience for new employees
- Make sure employees feel welcome and valued
Onboarding reduce the time to productivity for new employees, improve employee engagement, provide consistent and relevant information about the organization to the all employees and off course understand employee expectations and hence start helping building the relationship.
Recruiting on the other hand is the ability to successfully attract and hire key talent for current and future organizational needs through competency based advertising and interviewing efforts as hiring talented individuals is crucial to an organization’s success. But in order to hire the most talented, one must first recruit them and could be a challenging task. It is so true that a imperfectly designed recruitment process can miss captivating job candidates even those who work for the competitors because they can never find out the right position at the right time.
Recruitment process can support the talent acquisition by helping HR managers to research, source, communicate with and continuously engage the potential job candidates. The recruitment solutions market is significantly dynamic and current consumer technology innovations such as social media and video platforms have revolutionized talent acquisition tools. New recruitment strategy has really helps on effectively source candidates in today’s socially connected world.
Performance Management
If we follow the definition it states an ongoing, constant process of communicating and simplifying job responsibilities, priorities, performance expectations and development planning that optimize an individual’s performance and align with organizational strategic goals. Performance management is a crucial segment of maintaining the best possible talents as it enables companies not only to identify high performers and high potentials but also assist to understand the pitfall of under-performance. All these help companies to perform a better strategic decision on increasing excellence, retention efforts and to encourage talents.
When people hear about performance management, the annual review may be their first thought. However, a valuable performance management process involves much more than just the annual review. Starting from goal setting and development planning for the employees which generally take place beginning of the appraisal cycle, it should also include mid-year assessment to see employee’s progress and provide opportunities for improvement and at the end the process comes to annual review.
Many companies are also engaging into 360 assessment process as well. A 360 degree appraisal is a type of employee performance review in which direct reportees or subordinates, peers and line managers all anonymously rate the employee. Generally this information is then consolidated into that person’s performance review. Most organizations that focus on employee development use the 360 degree assessment tool to assess performance and potential of the employee and empower the employees to plan their career path based on the feedback.
Most organizations have still historically attached to an annual review process, where an employee generally have meeting with his manager to discuss strengths, goals and areas for the improvement. But today, HR managers are realizing that the performance management process itself needs some improvement.
In recent years, many companies have discarded the performance assessment based annual review in favor of a more persistent, educating-oriented model. Another significant trend in the performance management area is to involve more people in the review process, to get a more accurate picture of an employee.
Compensation Planning and Rewards
A way to remunerate individuals for important achievements, contributions to the goals of the career and improve skills and competencies in their jobs is often treat as compensation. There is a popular old saying, compensation isn’t the reason employees stay, but it can be the reason they leave. If companies want to keep their best employees around, they need an elegant approach to using compensation as a strategic tool for engaging them, while staying in line with company’s compensation standards, policies and guidelines.
Its main objectives are to:
- Reward employees in a regular manner for the important accomplishments in their jobs and career development
- Encourage career and professional growth
- Provide managers with flexibility in rewarding employees based on available resources and methodologies
- Being consistent with pay policies, the protocols and procedures of the organizations
In many organizations, compensation management is still handled in spreadsheet rather than dedicated solution. In addition to reducing manual effort and potential for errors, compensation management solutions adds visibility into bonuses and other employee rewards, which in turn enhance motivation and provide a proper platform for planning compensations.
Compensation is a method of appreciating; honoring, encouraging, and supporting individuals and teams who contribute, through behaviors and actions, to the success of the organization and in this way the rewarding can be used to strengthen the organizational values. It leads all employees for business success, or to recognize individual contributions toward that success.
Compensation is an important component of talent management strategy. To attract talent and remain competitive, organizations need to design a practical and cost-effective compensation plan that meets both the needs of their business and the market for talents.
Career and Succession Planning
Succession management is a process for recognizing and developing employees with the possibility to fill key or critical organizational positions. Succession Management actually means having the right people in the right jobs at the right time. In other words, it is an organized process to identify and grow individuals for potential future openings.
Companies need a right bench with the right future leaders who can drive their business strategy forward. The approach to talent management succession planning begins with the strategy and ends with a refined people and leadership plan. This help the leaders unveil organizational competencies and make sure companies have the right people for those important and critical roles that play such a big part in driving success.
Career planning state how the organization structures the career progress of their employees and the individual’s process for identifying career opportunities within an organization’s structure, and the right involvement in education, skills and experience building needed to achieve specific career goals.
Career and succession planning actually empowers organizations as they plan for the future. The proper way of career and succession planning increases visibilities by allowing organizations to easily identify and develop the top talent. In addition to preparing upcoming talent to move into key positions, it can effortlessly identify and rectify gaps in succession planning as well. It enhance employee engagement by generating proper career paths for them, along with supporting development plans which may be designed to fill the gaps and encourage employee growth using career development solutions.
Learning and Development
In the past the learning and talent management have worked independently of each other, but towards the same objective which is nothing but growing productivity. As technology continues to evolve, learning also becomes a part of talent management process, generating more streamlined and effective learning experiences that impact employee performance. Learning is using other talent management process, performance management in particular; to drive development plans, while succession management is using learning to prepare future leaders. All these integrated set of processes are changing development strategies and the way in which companies manage and assign learning content, ultimately improving performance.
Learning management systems has been used from long time to administrating courses and other traditional training programs. Experts say that corporate learning is now coming out beyond firm course delivery to a more natural and integrated experience. The companies are embracing new ways of employee development and reviewing new learning technology. Massive open online courses (MOOC), Self- paced online courses, Distributed open collaborative courses are evolving as the future of new learning options and becoming very popular way of learning. Companies are also focusing to integrate these possibilities into their learning management portfolio.
Development opportunities involve any opportunity that ensures that employees with an interest in and the potential for filling key positions are provided with the significant development opportunities.
Some of the challenging and interesting engagements that can be used as core developmental opportunities to build key strengths could be following:
- Leading a cross-functional team or group
- Working directly with senior leaders on a particular project
- Building a team from the starting
- Playing the role of a mentor
- Inclusion on a major strategic initiatives
- Accepting a transfer or rotational assignment
- Being promoted to a new challenging role.
Eventually there are much of speculations around these terms and definitions results from the fact that talent management is quite new and a final definition of it have not yet been agreed upon. While some people think it refers to managing all the employees at a company, others think it only refers to the top performers.
These integrated supports for strategic employee management processes can help companies find the best talents for their business develop and leverage their talent, align their efforts with the corporate objectives and maximize the effect of employee training and developments. Organizations can retain, motivate and promote top performers through the right balance of compensation, benefits and career development programs.
All these integrated set of processes are actually providing big opportunities and advantages to the organizations and guide them to the success. Some of the advantages of effective Talent Management are:
- Organization’s effectiveness and productivity can improve continuously.
- Helps in achieving the business goals with high quality performance.
- Improves organization’s overall culture and work environment.
- Employees are more satisfied.
- Retention of talent get improves and turnover goes down.
- Better overall growth of talents associated with the organization.
Talent management is an important aspect of broader human capital management (HCM) initiatives and human resources department plays a significant part in it.
According to Bersin & Associates around twelve years ago (2004) people in HR started talking about bringing together many of the standalone practices within HR into a new function called “Talent Management.” At that point in time the economy was growing and pundits were talking about “The War for Talent.” The challenges included aging baby boomers, a tight economy for critical skills, and the need to build leaders around the world. This set of issues refocused HR on building talent programs to recruit, develop, and better manage people.
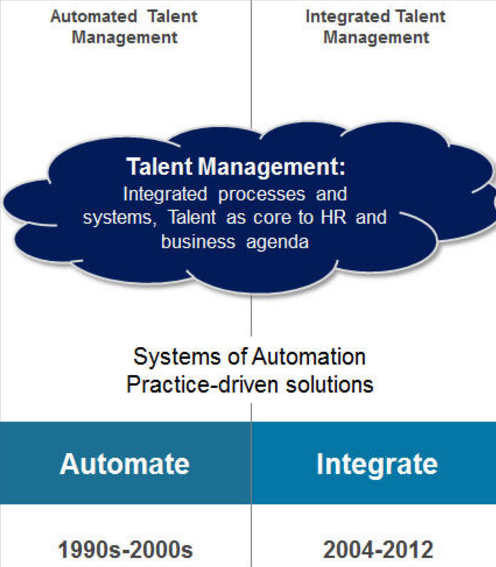
(Picture taken from Bersin & Associates)
Talent challenges on recruiting, onboarding, succession planning, leadership and development pushed HR to think differently. Rather than define itself as the “service center for employee issues” and a “service center for managers,” HR started to redefine itself as the “talent management function” for business. This was a profound shift and it set off ten years of restructuring, re skilling, and redesigning the HR function.
Integrated Talent Management was evolved and most of the software vendors start building these suites or a package on integrated talent management. The goals of integrated talent management were lofty: give companies an integrated view of capabilities, leadership gaps, succession pools, and even talent needs for the future. Even today this is a tough thing to do, but we have built an industry around this whole idea.
In a global and competitive workplace, the skills of human resources professionals are becoming more critical than ever especially for the talent managers. It is not enough for talent managers simply to be effective administrators as of today, company’s CEOs and executive management expect their talent leaders to deliver the fruitful skills that drive innovation, develop talent and leadership, transform the organizational culture and enhance the productivity.
Human resources management has mature over the past in response to changes in the way companies work. So far HR’s role in many organizations has been largely reactive, adapting the talent to the growth of the business. But HR has gradually improved significantly in its role and contributions to the organization.
As the role and consequence of the HR profession has advanced from transactional to strategic, HR professionals needs to develop skill sets which help employees to fulfil the long-term goals of the business.
While many current HR practices still moving around traditional business of recruiting, onboarding, training and development, the management of human resources generate real value by focusing on a company’s most valuable resource: the undeveloped potential of its talent. This dedication provides a distinctive competitive advantage over talents and organization‘s business model.
Human resource management strategy capitalizes for talent model as well in an integrated way and develops better possibilities for the organizations:
Retaining key employees:
One of the considerable challenge human resource management facing today is the development of an successful HR strategy that aligns and supports organization’s business goals. Even today employers are still facing a shortage of applicants with the right skills and experience to fill critical jobs. Lower employee engagement makes it more challenging, putting companies at risk of losing important talent. Hence retaining key employees should be a top priority for effective talent management that supports organization’s human resource management strategies and overall corporate objectives.
Increasing employee engagement:
Reports published in the past already reveals that employee engagement is at the lowest level in last few years, which in turns automatically increase the employees attrition rates. On the other hand research by Bersin and Associates shows that organizations with a deliberate and defined process for identifying high potential employees are seven times more effective at delivering business results. Using the right processes in place to identify, manage, develop, and reward top talent with in-demand skills are the strategic priority for human resource management which also increases employee engagements.
Generating future potential:
Talent model uses HR strategy as a key across all talent management processes to drive business success. A successful talent management requires involvement around performance, key talent, critical roles, potential and future success to align business strategy and overall business goals. HR managers plays an important role by improving corporate policies and changes in achieving performance turnover which impact hugely on an organization’s success, especially when the turnover involves top performers. All these generate a high potential for the future talent management strategy and business productivity.
The role of human resources within the corporate structure has changed significantly over the years. Human resources departments generally involved in overall business strategy like organizational development through training, leading business communications and developing compensation models. Though HR departments focus on these strategic goals, there has been always shift towards talent management. Talent management establishes new strategic goals to streamline hiring and leadership succession processes using the employee lifecycle model. Talent management is a key component to business success in the current economy as it allows companies to retain top talent while increasing productivity.
But the talent management differs from the HR or traditional way of working. Talent management actually vary from previous HR processes for hiring, training, and retaining employees and indeed from HR itself in several ways:
- Processes like hiring, training and retention before were centralized in the HR team, and with talent management many of these processes are associated to the line managers to lead the employees. In this way the entire organization is responsible and has a support in these activities.
- HR is more administrative focused like dealing with pay, vacation days, benefits, complaints, policies, while talent management is almost extremely focused on helping and improving the top talent in the organization.
- Talent management is strategic, exhibiting as an organization wide long term plan associated with overall business goals, while HR is more tactical, dealing with the day to day management of people.
Talent management’s role in organization’s business strategy changed the game of HR business. Slower economic growth join with a shortage of talent to fill crucial positions, the rise of social networking and a new generation with digital world and increased expectation from the top management, actually means he days of transactional HR have long passed. And to make sure and able to make this jump from transactional to strategic, HR leaders need greater focus on tools, processes, integration and should start addressing talent management into HR strategies.
After embrace new talent management applications, most organizations realize the need for integration. Apart from process integration technology investments are often made to streamline processes and improve data accuracy. But the full potential of integration cannot be realized when companies have multiple systems of record with disconnected data streams and conflicting processes. A study shows that HR has a long way to go when it comes to integration. The majority of organizations surveyed report poor to moderate integration of their talent management applications. Some processes are a bit more likely to be well integrated than the other pillars of talent management, although even there the number with poor integration is more than those with good integration.
It is very important to know the future business trends, and new vision for the human resource strategy and objectives to handle talent managements and possibilities for improvements of the current solutions.


