The biggest challenge that is occurring now due to the growing digital economy, is about to build a digital-ready workforce in an evolving business environment. To do that, any organization must start with filling the talent gap in technological skills, which is also vital to digital strategy. Successfully acquiring, developing and deploying talent starts with a strategy that directs what work will be done, how it will get done and by whom.
Organizations need to create a compelling value proposition for talent that includes training in new skills, development opportunities, and rewards. For leaders, retaining the human part in a growing digital world is vital for future success. It turns clear that the digital age requires different qualities from business leaders. The leaders who understand well enough to see how technology and people complement each other and create added value are on the front line.
Today, leaders should be able to connect with a well-defined purpose, inspire their workforce for this common purpose and give them the independence to create more value. When the workforce gets a purpose to deliver, motivated and inspired by leaders, they respond with high levels of engagement, increase commitment, bring creativity to work, shape themselves and their organizations, to flourish in a digital age. And all these are becoming a vital aspect of the growing, new talent economy.
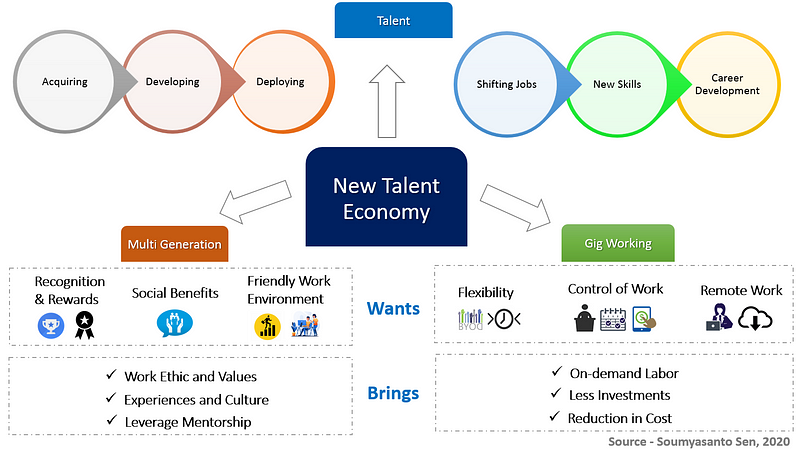
New Talent economy
The fourth industrial revolution is having a significant effect on other socio-economic and demographic aspects to create disruptions of business model change in almost all industries, which in turn making a major change in the labor markets. And that led to emerging of a new set of jobs, partly or completely displacing others. The skill demand required in both old and new jobs is also changing most industries and transform how people work.
These shifting of the jobs and changing of the skills are growing at a vast rate, and this job transformation is also impacting the nature of work dramatically. Different patterns of work, the diverse structure of employment contracts including payments, and an increasing passion for flexibility have also transformed concurrent working relationships. As the world of work continues to transition, a new economy has been derived; and the gig economy has emerged as a key driver of this change.

Gigs are typically not full-time workforce who lack long-term commitment from the organizations. Their working hours are unpredictable, with arrangements usually being highly-flexible and totally dependent on the demand at any given time. The gig economy or freelance work has gained traction in the last many years, especially within the young workforce. And the gig economy is growing and changing the way we work.
Organizations operating in the gig economy usually use new online digital platforms that connect customers directly for providing the services by the workforce who are working more as independent, rather than employees. These workforces are looking for high flexibility, more control of their own work and like to work remotely in most cases, with minimal commitment with these organizations. And gig workers are usually paid for each individual task they complete.
Many of them, who earn income through these online digital platforms, only do it for a few months each year. One reason is that some portion of the workforce who experimented with gig work usually landing with conventional jobs as the economy got to shift from time to time. These also led to the growth of the other new economies; the rise platform economy and shared-economy have a quite overlap with the gig economy.
On top of this, the changing population dynamics in emerging and developed countries have led to a surge in the proportion of the young population entering the labor market, which also contribute to urbanization and providing to international migration. Many young people are starting their working lives in less secure and stable forms of employment.
These young respondents preferring flexible work schedules to be important, along with they find more values in owning their work and get paid for their tasks done than any conventional forms of employment, such as good incomes, opportunities for career development and social benefits. As their participation in the gig economy and startup ecosystems continues to rise, many organizations are turning toward the growing alternative workforce segment and pursuing to hire more of these workers.
One common aspect, irrespective of generations and workers type, whether it’s independent or traditional jobholders or any demographic diversity is that the current and future workforce will have to become more proactive about managing their skills. As drift like technological growth, interconnectivity, collaboration, and increased individual responsibility begin to transform the way we live and work.
Impact and preparation for new talent
The digital revolution is having a very significant impact on the workforce and HR organization. And the major changes include ongoing demographic, technological, sociological and cultural transformations. In this digital era, where technology is also changing as the fastest it can, HR and business leaders should start streamlining themselves in terms of collaborating and considering the right work models for the workforces in respect to that.
In this digital era, the demand of the talent is not just driven by the technological need; many organizations are transforming their business models, focusing on more customer-centric approaches, proceeding with digital integrated operations, and they need talent not only with the right skills but also with the ability to enabling these changes and collaborating in more agile ways.
Today, the new generation workforce makes it more challenge for the organizations, as their expectation from their employers and jobs is quite different from the previous generations. While the previous generations possess more value on security and tradition, new generations are more motivated by personal happiness, attaining aspirations, and recognition. They also expect higher flexibility, more adaptable career paths, a clear work-life balance, and a defined purpose.
The changing demographics and skills requirements in the talent markets make top talent effectively insufficient for the organizations, and hence many organizations are looking for innovative ways to access talent. Many organizations are becoming more experimental to a growingly complex and diverse talent ecosystem, by taking advantage of the communities.
Organizations should establish a more successful, wider and higher-quality talent pipeline by collaborating across others by enlarging the existing talent base and leveraging talent ecosystems by sharing talent more effectively within and across organizations, this is similar also for talent acquisitions, development, and retention. These communities are driven by collaborations, learning, networking, partnership, and many other factors.
Leveraging knowledge and personalization, aligning the employee value proposition, and syncing employee’s purpose with the company’s vision, business strategy, and operating model are some crucial factors for the organizations in their successful journey. Other than the value propositions, many agile and innovative organizations are developing new talent acquisition models that can reflect the current digital age by winning the talent war and progress towards success.
A successful talent acquisition models should be built on collaboration, sharing, and community building strategy. The war for talent can only be won by adopting this new mindset and embracing the concept and the competitive advantage of open source talent ecosystem. Many organizations are already investing in their workforces when there is a question about talent, and this investment becomes more effective once the organization starts understanding the importance of human and social capital within that ecosystem and communities.
The HR Readiness for future
In the new talent economy, HR leaders and professionals need to focus in helping the business to understand the skills demand and preparation for the future and ensure to provide an astonishing experience for these workforces so that they can to learn the new ways of engaging, continuous learning techniques and encouraging collaboration with other people and machines. And all these needs a new environment in which they can work, learn, motivate and grow.
Workforces are becoming more geographically diverse as more young generations workers are moving to bigger cities and successful countries for their work. In addition, we notice the rise of remote workers in the workforce landscape as well. All these again certainly demand a well-articulated approach framework for HR readiness for the new talent economy and future of work.

The above figure also describes the four main elements of the HR readiness to help organizations to get prepare for, they are:
· Providing the continue learning and development opportunity to the employees in the organizations, by investing in different employee education, cross trainings, lateral moves and internship programs.
· Adopting new mindsets, technologies, and skills to lead the way in the world of work, as future needs both technical and social skills for the workforce.
· Demand for the redesigning of both business processes and ways of working, which need a sense of urgency throughout the job transformation and career development for the workforces.
· Start building a collaborative work environment for two different segments of workforces, humans, and machines, due to a high increase in the automation and augmentation of the human tasks and activities by the machines.
HR organization should expect these changes across the globe soon or later and that trigger more expectations towards increasing for benefits, mobility, flexible work and a new way of work possibilities. Due to the shift of changing skills and job transformation, the number of workers in different levels of skills will also be going to change. And that needs some set of preparation and balance so that there could be a constant increase in employee engagement, retention and productivity.
New skills shortages are on the rise due to the rapid change in technology and business which led to many challenges in finding the right skilled worker for the organization and this also creates instability in the labor market, especially if we include the job transformation landscape. Some mitigation what HR organization here can do is also depend on the business leaders, as they are responsible for their workforces.
There is a need for more partnering opportunities with learning institutions, to uplift more education and training for the needed skills. On top of this, offering more internships programs, getting stronger with the talent pools and contributing towards workforce developments are also important to consider for the HR organizations.

For further interest and insights over this topic, buy your copy today to understand a broader Digital HR Strategy ‘Digital HR Strategy — Achieving sustainable transformation in the digital age’
Originally published in digitalhrtech


